Metrics Glossary
Overall
Count Total count of feedback records, summing all ingested sources. Empty feedback, with little or no comment, will be counted.
Relevant Feedback Count Total count of relevant feedback records, summing all ingested sources. Empty, unreadable, or incomprehensible feedback will not be counted.
%Count Percentage of feedback filtered by a specific criterion relative to the organization's total feedback count. Example: If 100 is the count of feedback after applying a filter and 200 is the organization's total, the % count will be 50%.
Sentiment Score The sentiment score is calculated by subtracting the total number of negative feedback from the total number of positive feedback. Example: A sentiment score of +80 indicates satisfaction. A sentiment score of -20 indicates dissatisfaction.
%Count Over Area Percentage of feedback, given a filter, relative to the total feedback count in a specific area. Example: An opportunity with 100 feedback records in an area with 5,000 feedback records will have a % count over the area of 2%.
%Count Over Collection Percentage of feedback, given a filter, relative to the total feedback count in a specific collection. Example: An opportunity with 100 feedback records in a collection with 10,000 feedback records will have a % count over the collection of 1%.
Impact Score The impact score indicates the average dissatisfaction of a specific theme across the company's various channels. Weight: W1, W2 … Wn Source: S1, S2 … Sn
Formula:
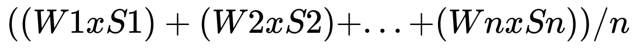
Tickets
Potential saving Count of tickets in an Area or Opportunity, multiplied by the "unit service cost" defined in "Organization Settings." Example: A count of 10,000 tickets with a unit service cost of $5.00 results in a potential saving of $50,000.
Contact rate The ratio of tickets to the number of active customers. Example: In a given month, 100,000 tickets were created, and there are 100,000 active customers. The contact rate is 100%.
TCSAT Count Absolute count of CSAT tickets. Example: Tickets with little or no comments are counted.
%TCSAT Count Percentage of CSAT tickets filtered by a criterion relative to the organization's total. Example: If 100 is the CSAT ticket count after applying a filter and 200 is the organization's total count, the %TCSAT Count is 50%.
TCSAT Score The score of positive responses (4 or 5) relative to the total number of responses. Example: A CSAT score of 50 means 50% of the responses received a score of 4 or 5.
TNPS Count Absolute count of NPS tickets. Example: Tickets with little or no comments are counted.
%TNPS Count Percentage of NPS tickets filtered by a criterion relative to the organization's total. Example: If 100 is the NPS ticket count after applying a filter and 200 is the organization's total count, the %TNPS Count is 50%.
TNPS Score The score is calculated as %Promoters − %Detractors. Example: If 20% are promoters and 40% are detractors, the NPS score will be -20.
Social Media Posts
Unsatisfied Count Absolute count of posts containing negative comments.
%Unsatisfied Percentage of unsatisfied posts relative to all the organization's posts. Example: If 10 people post negative feedback out of 100 posts, the %Unsatisfied is 10%.
%Unsatisfied over Collection Percentage of unsatisfied posts (with negative comments) relative to the total number of posts in a collection. Example: If 10 people post negative feedback out of 200 posts in a collection, the %Unsatisfied is 5% for that collection.
%Unsatisfied over Area Percentage of unsatisfied posts (with negative comments) relative to the total number of posts in an area. Example: If 10 people post negative feedback out of 200 responses in an area, the %Unsatisfied is 5% for that area.
%Unsatisfied Count/All Comments Percentage of unsatisfied posts relative to all posts in the organization that contain comments. Example: If 10 people post negative feedback out of 100 posts (with comments), the %Unsatisfied is 10%.
%Unsatisfied Count/All Area Comments Percentage of unsatisfied posts (with negative comments) relative to the total number of posts with comments in an area. Example: If 10 people post negative feedback out of 200 responses (with comments) in an area, the %Unsatisfied is 5% for that area.
%Unsatisfied Count/All Collection Comments Percentage of unsatisfied posts (with negative comments) relative to the total number of posts with comments in a collection. Example: If 10 people post negative feedback out of 200 posts (with comments) in a collection, the %Unsatisfied is 5% for that collection.
NPS
Score The score is calculated as: %Promoters − %Detractors. Example: If 20% are promoters and 40% are detractors, the NPS score will be -20.
%Det./Detractors Percentage of NPS detractors (score 0 to 6) in a filter relative to the organization's total detractors. Example: In a collection, area, segment, or opportunity with 10 detractors out of 100 detractors in the organization, the value will be 10%.
%Pro./Promoters Percentage of NPS promoters (score 9 or 10) in a filter relative to the organization's total promoters. Example: In a collection, area, segment, or opportunity with 10 promoters out of 100 promoters in the organization, the value will be 10%.
%Neu./Neutrals Percentage of NPS neutrals (score 7 or 8) in a filter relative to the organization's total neutrals. Example: In a collection, area, segment, or opportunity with 10 neutrals out of 100 neutrals in the organization, the value will be 10%.
%Detractors/All comments Percentage of detractors (score 0 to 6) relative to all NPS responses in the organization that contain comments. Example: If 10 people gave scores between 1 and 6 out of 100 responses with comments, the %Detractors is 10%.
%Promoters/All comments Percentage of promoters (score 9 or 10) relative to all NPS responses in the organization that contain comments. Example: If 10 people gave scores 9 or 10 out of 100 responses with comments, the %Promoters is 10%.
%Neutrals/All comments Percentage of neutrals (score 7 or 8) relative to all NPS responses in the organization that contain comments. Example: If 10 people gave scores 7 or 8 out of 100 responses with comments, the %Neutrals is 10%.
%Detractors/All responses Percentage of detractors (score 0 to 6) relative to all NPS responses in the organization. Example: If 10 people gave scores between 1 and 6 out of 100 responses, the %Detractors is 10%.
%Promoters/All responses Percentage of promoters (score 9 or 10) relative to all NPS responses in the organization. Example: If 10 people gave scores 9 or 10 out of 100 responses, the %Promoters is 10%.
%Neutrals/All responses Percentage of neutrals (score 7 or 8) relative to all NPS responses in the organization. Example: If 10 people gave scores 7 or 8 out of 100 responses, the %Neutrals is 10%.
%Detractors/All area Percentage of detractors (score 0 to 6) relative to all NPS responses in an area. Example: If 10 people gave scores between 1 and 6 out of 200 responses in an area, the %Detractors is 5%.
%Detractors/All area comments Percentage of detractors (score 0 to 6) relative to all NPS responses in an area that contain comments. Example: If 10 people gave scores between 1 and 6 out of 200 responses (with comments) in an area, the %Detractors is 5%.
Detractors count Absolute count of NPS responses with a score from 0 to 6.
Neutrals count Absolute count of NPS responses with a score of 7 or 8.
Promoters count Absolute count of NPS responses with a score of 9 or 10.
Potential improvement Potential improvement in the NPS score if detractors and neutrals become promoters.
Potential improvement over collection Potential improvement in the NPS score if detractors and neutrals become promoters in a specific collection.
CSAT
Score Percentage of positive responses (4 or 5) relative to the total responses. Example: A CSAT score of 50 means that 50% of the responses had a score of 4 or 5.
AVG Rating Sum of all received scores divided by the total number of respondents. Example: If one person gave a score of 1 and another gave a score of 5, the AVG Rating is 2.5.
Unsatisfied Count Absolute count of responses with a score of 1 or 2.
Neutrals Count Absolute count of responses with a score of 3.
Satisfied Count Absolute count of responses with a score of 4 or 5.
%Unsatisfied Count/All Comments Percentage of unsatisfied responses relative to all CSAT responses in the organization that contain comments. Example: If 10 people gave low scores (1 or 2) out of 100 responses (with comments), the %Unsatisfied is 10%.
Reviews
AVG Rating Sum of all received ratings divided by the total number of reviews. Example: If one person gave a rating of 1 and another gave a rating of 5, the AVG Rating is 2.5.
Unsatisfied Count Absolute count of reviews with 1 or 2 stars.
Neutrals Count Absolute count of reviews with 3 stars.
Satisfied Count Absolute count of reviews with 4 or 5 stars.
%Unsatisfied Count/All Comments Percentage of unsatisfied reviews (1 or 2 stars) relative to all reviews in the organization that contain comments. Example: If 10 people gave ratings of 1 or 2 out of a total of 100 reviews, the %Unsatisfied is 10%.
%Unsatisfied Count/All Area Comments Percentage of unsatisfied reviews (1 or 2 stars) relative to all reviews with comments in a given area. Example: If 10 people gave ratings of 1 or 2 out of a total of 100 reviews (with comments) in the area, the %Unsatisfied is 10%.
%Count Over Area Percentage of reviews from a filter relative to the total reviews in a given area. Example: An opportunity with 20 reviews in an area with 100 reviews will have a %Count Over Area of 20%.
Segments
Opportunity Prevalence Rate Percentage of the opportunity in the segment divided by the percentage of the opportunity in the organization. Example: If an opportunity appears in 10% of the feedback within a segment and in 2.5% of the feedback across the organization, then the prevalence rate is 4. This indicates that the chance of the opportunity occurring in the segment is 4 times higher than expected in the workspace.
Prevalence Difference Percentage of the opportunity in the segment minus the percentage of the opportunity in the organization. Example: If an opportunity appears in 10% of the feedback within a segment and in 2.5% of the feedback across the organization, the prevalence difference is 7.5%. This indicates that the prevalence of the opportunity is 7.5% higher than expected in the organization.
Last updated